Understanding Phlebotomy: Your Guide to Blood Collection and Medical Diagnostics
If you’ve ever had blood drawn at a clinic or hospital, you’ve experienced teh vital process of phlebotomy. But what exactly does this medical procedure involve? How do professionals ensure accurate results and patient safety? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about blood collection, its meaning in medical diagnostics, and tips for those interested in pursuing a career as a phlebotomist. Whether you’re a patient, a healthcare student, or just curious, this article will demystify the world of phlebotomy.
Table of Contents
- What Is Phlebotomy?
- Importance of Phlebotomy in Healthcare
- Blood Collection Techniques
- Training and Certification for phlebotomists
- Benefits and Practical Tips
- Case Studies: Real-World Phlebotomy
- First-Hand Experience and Patient Viewpoint
- Conclusion
What Is Phlebotomy?
Phlebotomy is the process of making a cut or incission in a vein with the primary goal of drawing blood for laboratory testing, transfusions, research, or donation. The term originates from Greek – phlebo meaning vein and tomy meaning incision.
This medical procedure,often performed by innovative healthcare professionals called phlebotomists,is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics. Accurate blood samples are essential for diagnosing diseases, monitoring treatment effectiveness, and conducting medical research.
Importance of Phlebotomy in Healthcare
Blood testing plays a crucial role in diagnosing hundreds of health conditions. Here are some reasons why blood collection through phlebotomy is essential in healthcare:
- Diagnosis of Diseases: From infections to chronic illnesses like diabetes, blood tests provide critical information for diagnosis.
- Monitoring Treatment: Regular blood tests track the progress of treatments and medication efficacy.
- Blood Donation: Ensures safe blood supplies for transfusions.
- research and Growth: Blood samples help develop new medical therapies and understand disease mechanisms.
Blood Collection Techniques
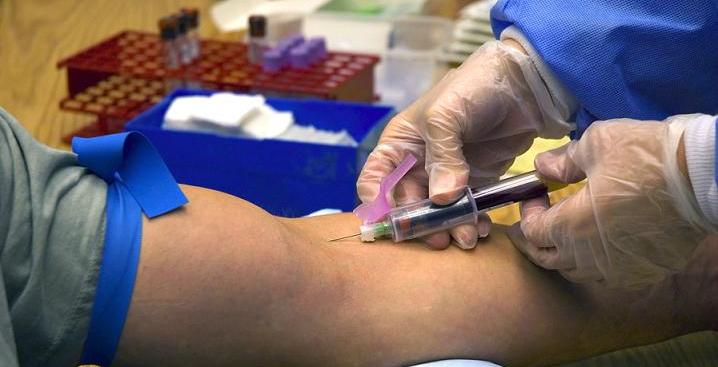
1. Venipuncture
The most common method, involving inserting a needle into a vein-usually in the arm or hand-to obtain blood.ItS preferred for larger blood volumes and reliable sampling.
2.Capillary Collection
Using a lancet to prick the fingertip or heel (for infants) for small blood samples, often used for blood glucose or newborn screening tests.
3. Arterial Puncture
Less common, performed to assess oxygen levels in arterial blood, typically in critical care settings.
| Method | Uses | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| venipuncture | Major blood tests, transfusions | Reliable, efficient | Requires skill |
| Capillary | Blood glucose, neonatal testing | Minimally invasive | Limited volume |
| Arterial | Oxygen levels | Precise measurements | Complex, painful |
Training and Certification for Phlebotomists
Becoming a skilled phlebotomist requires proper training and certification. Many healthcare institutions and technical schools offer programs that cover:
- Venipuncture and capillary collection techniques
- Patient identification and interaction skills
- Infection control and safety protocols
- Handling and processing blood samples
Certification requirements vary by region but generally include completing a training program and passing an exam. Certified phlebotomists are frequently enough preferred by employers, as certification signifies competence and adherence to safety standards.
Benefits of Proper Phlebotomy and Practical Tips
Benefits:
- Ensures accurate test results
- Minimizes patient discomfort and risk
- Reduces sample contamination
- Maintains safety for healthcare workers
Practical Tips for Triumphant Blood Collection:
- Prepare the patient: Explain the procedure clearly to reduce anxiety.
- Select the right vein: Usually the median cubital vein in the arm.
- Use suitable equipment: Sterile needles, tourniquets, and collection tubes.
- Maintain hygiene: Follow infection control protocols.
- Be gentle: Minimize discomfort and avoid collapsing veins.
Case Studies: Real-World Phlebotomy
| Scenario | Challenge | outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Pediatric Blood Draw | Child was anxious; veins hard to locate | Used distraction techniques; successful sample collection |
| Diabetic Patient | Need for quick glucose testing | capillary pinprick; fast and accurate results |
| Anticoagulant Blood Sample | Proper tube handling required | Followed protocol; high-quality sample |
First-Hand Experience and Patient Perspective
Many patients find blood draws intimidating, but with professional skill and empathy, phlebotomists can provide a comfortable experience. From a patient’s view, a gentle puncture, clear instructions, and reassurance go a long way in reducing anxiety.Hearing positive feedback from patients can inspire confidence and improve overall healthcare experience.
Conclusion
Phlebotomy is a vital component of modern healthcare, enabling accurate diagnostics, safe blood transfusions, and groundbreaking research. Whether you’re considering a career as a phlebotomist or wont to understand the blood collection process better as a patient, knowledge about blood collection techniques, safety protocols, and the importance of proper training is essential. By understanding the nuances of phlebotomy, you contribute to better health outcomes and support the foundation of effective medical diagnostics.
If you’re interested in becoming a certified phlebotomist or seeking quality blood collection services, ensure you choose trained professionals committed to safety and accuracy. Remember, skill and compassion are the cornerstones of successful phlebotomy!